Confidentiality breaches during M&A transactions can derail deals, lower valuations, and create regulatory headaches. Leaks of sensitive information – like pricing strategies or customer data – can harm negotiations, disrupt operations, and even result in penalties for compliance violations.
Here’s a quick summary of how to handle these breaches effectively:
- Detect Fast: Monitor virtual data rooms (VDRs) and access logs for anomalies like unusual file downloads or login attempts.
- Assess the Impact: Identify who accessed the data and evaluate risks to finances, reputation, and compliance.
- Contain the Damage: Revoke access, secure systems, and notify stakeholders promptly.
- Investigate Thoroughly: Trace the source of the breach, preserve evidence, and fix vulnerabilities.
- Prevent Future Issues: Strengthen security protocols, enforce stricter access controls, and train teams on confidentiality best practices.
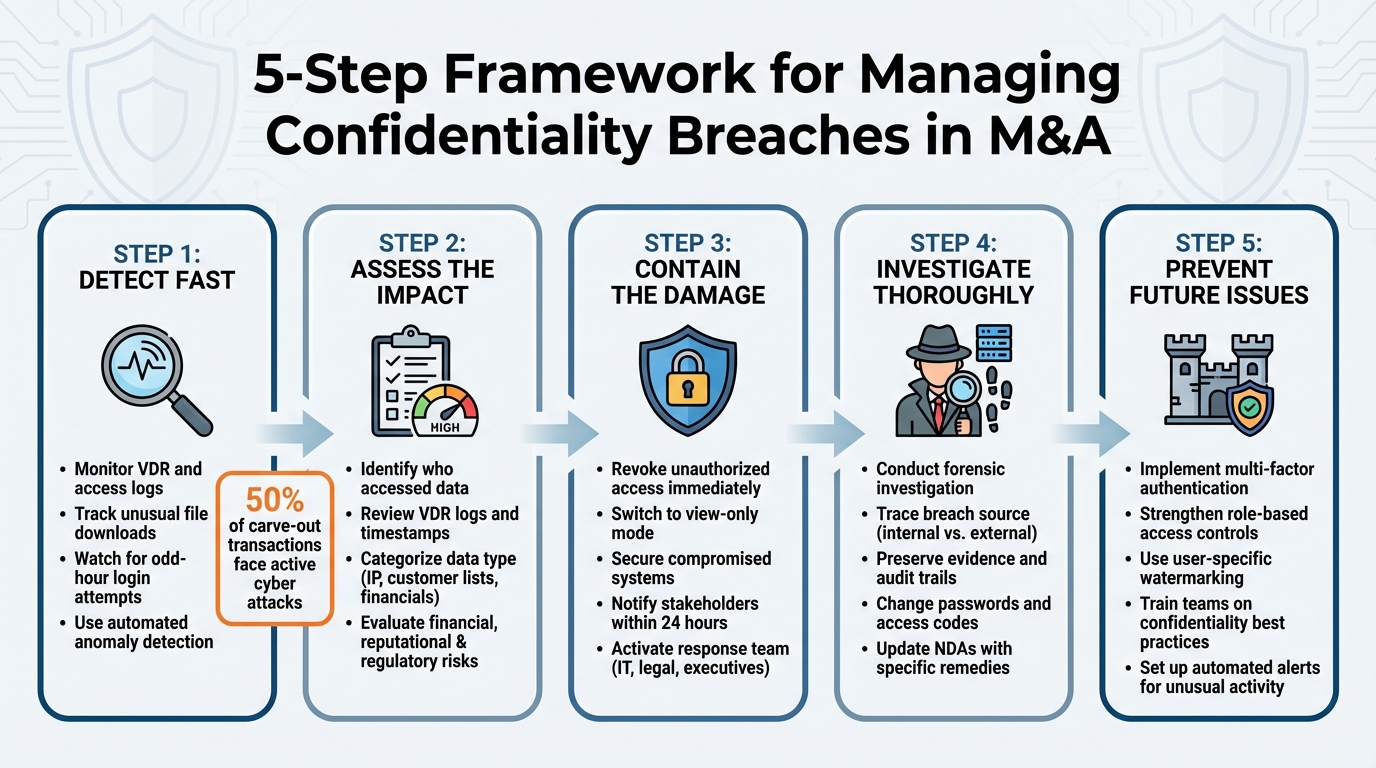
5-Step Framework for Managing M&A Confidentiality Breaches
Step 1: Detect the Breach Quickly
Keep a Close Eye on Virtual Data Rooms and Access Logs
The first step in safeguarding confidential information is constant vigilance over your virtual data room. This means tracking every access event: who viewed the files, when they did, how long they stayed, and any unauthorized attempts to gain entry.
Automated systems that detect anomalies in real-time are invaluable here. These tools can send immediate alerts for suspicious activities – like login attempts from unusual locations or excessive downloads by unauthorized users. For example, if a junior analyst downloads 50 files late at night, it’s a red flag that demands swift investigation.
User-specific watermarking adds another layer of security. By embedding each viewer’s name and IP address directly onto documents, you can quickly trace any unauthorized sharing. For highly sensitive information, particularly when competitors are involved, it’s wise to disable download permissions entirely and switch to "view only" mode. This approach ensures reviewers can access the data without the risk of physical theft.
When monitoring reveals irregularities, it’s crucial to act promptly and dig into the specifics of any unusual activity.
Spot the Red Flags During M&A Processes
Recognizing the warning signs of a breach early can make all the difference. Look for unusual file access patterns, such as attempts to view restricted folders, large-scale downloads of sensitive trade secrets by unauthorized individuals, or login activity during odd hours. Pay close attention to any download attempts on documents marked as "view only."
External clues can be just as telling as internal logs. If rumors begin to circulate among suppliers, key customers, or lenders before any official announcements, it’s often a sign that too many people have been brought into the loop or that sensitive information has been leaked. Even minor incidents should trigger your breach-response protocol within 24 hours.
"Threat actors time their attacks around live transactions. We’ve seen businesses hit with ransomware exactly when disruption will hurt the most." – Vinod Bange, Data and Cybersecurity Partner, Baker McKenzie
The stakes couldn’t be higher. Nearly 50% of carve-out transactions face active cyber attacks during the deal process. This makes early detection not just a good idea but an absolute must for preserving the value of the deal.
Step 2: Determine the Scope and Impact
Identify Who Accessed the Information
After discovering a breach, the first step is to pinpoint exactly who accessed the confidential data. Use detailed VDR logs to track every interaction – this includes identifying who viewed specific documents, when they logged in, how long they spent, and whether they downloaded or altered any files.
Implementing role-based access controls can significantly narrow down the list of potential suspects. These controls limit information visibility based on user roles, reducing the pool of individuals who might have accessed sensitive data. To confirm legitimate access, cross-check personnel logs against VDR activity. For particularly sensitive deals, review your "clean team" list – these are individuals excluded from competitive decision-making – to ensure no unauthorized access occurred.
Watermarks can be a powerful tool for tracing leaks. These embedded identifiers, which include details like the viewer’s name and IP address, allow you to link leaked files directly to the responsible party. This applies to both digital versions and physical printouts, making it much harder for anyone to cover their tracks.
There’s a cautionary tale here: a recent case showed how granting overly broad access during early diligence can lead to premature public disclosures.
Once you’ve identified the individuals involved, it’s time to evaluate the risks the breach poses – financial, reputational, and regulatory.
Assess Reputational, Regulatory, and Financial Risks
Knowing who accessed the data is just the beginning. The next step is to assess the potential damage by understanding what type of information was leaked. Start by categorizing the data: Was it intellectual property, customer lists, or financial projections? The sensitivity of the information will dictate the potential harm, such as competitive disadvantages or the loss of proprietary knowledge.
Financial risks often emerge first. Leaked data can weaken negotiating leverage, lower the target company’s valuation, or even expedite deal closures at a disadvantage. For example, if pricing strategies or customer contracts fall into competitors’ hands, they could use that information to undercut your position. Beyond the immediate financial implications, breaches can also damage employee morale, disrupt customer relationships, and erode supplier trust – all of which can destabilize operations during a critical transition period.
Regulatory risks add another layer of concern. For public companies, the stakes are particularly high. If sensitive terms from a confidential agreement become public, even by accident, you may be required to file an updated, unredacted version of the exhibit with the SEC.
"Public disclosure – inadvertent or otherwise – could obligate a company to file with the SEC a revised version of the exhibit that includes the publicly disclosed information".
| Risk Category | Potential Impact | Assessment Method |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Reduced valuation, loss of competitive edge, costs from expedited deal closures | Review market response and negotiating position |
| Reputational | Decline in employee morale, customer dissatisfaction, and loss of trust | Monitor internal and external feedback |
| Regulatory | SEC scrutiny, mandatory refiling of sensitive documents | Review SEC exhibit rules and compliance guidance |
Antitrust violations are another serious concern. If operational staff accessed competitively sensitive information before the deal officially closed, you could face "gun-jumping" penalties from the DOJ or FTC. These fines have reached into the millions in past cases. To prepare for potential regulatory reviews, document every step of your investigation thoroughly.
How to Prevent and Manage a Data Breach in Your Business | LegalVision UK
Step 3: Contain the Breach and Notify Stakeholders
Once a breach has been detected and its scope assessed, the next step is to act quickly to limit the damage and ensure clear communication with all relevant parties.
Revoke Access and Secure Sensitive Data
When a breach is confirmed, time is of the essence. Start by isolating the affected systems to prevent further infiltration. Create forensic images to preserve evidence and immediately disconnect compromised systems from your network. Remove any malicious software that may be contributing to the breach.
Restrict access to your Virtual Data Room (VDR) by switching permissions to view-only and disabling downloads. Update all associated credentials and physical security protocols. Review and tighten role-based permissions, ensuring only essential personnel have access to sensitive data. If your primary IT systems are compromised, shift all breach-related communications to secure, encrypted channels.
Activate your response team, including IT, legal, and executive members, without delay. Engage legal counsel to ensure you’re meeting all regulatory and notification requirements. Taking these steps quickly helps contain the situation and lays the groundwork for effective communication.
Communicate with Stakeholders and Legal Teams
Once your systems are secured, focus on managing the fallout by coordinating with all stakeholders. Tailor your notifications based on the nature of the breach and the parties affected. Internally, inform your response team, executives, and legal counsel immediately to streamline the response plan. If personal data, such as Social Security numbers, has been exposed, notify affected individuals in compliance with applicable laws. Depending on the type of data and your industry, you might also need to inform regulators like state Attorneys General, the SEC (if you’re a publicly traded company), or other relevant authorities.
Contact key counterparties by phone to establish a consistent narrative, then follow up with written communication. Assign a single spokesperson to handle all media and law enforcement inquiries to maintain a unified message.
If third-party data is involved, promptly notify the data owners to encourage collaboration and minimize potential harm. Keep in mind that law enforcement may request a delay in public notifications if disclosure could interfere with an ongoing investigation.
sbb-itb-798d089
Step 4: Investigate and Fix the Problem
After containing the issue and informing stakeholders, the next step is digging deep into the situation to ensure the deal’s integrity is restored and safeguarded for the future. This process involves a thorough investigation and actionable fixes to address both immediate and long-term concerns.
Conduct Forensic Investigations
Start by identifying which systems were compromised – this could include virtual data rooms (VDRs), servers, or devices. Map out the timeline of events, from the initial breach to its detection, and determine whether the breach was caused by internal or external factors, as well as if it was intentional or accidental.
Preserve all forensic evidence. This includes creating system images, isolating affected machines, and maintaining a meticulous log of every action taken. Use audit trails to confirm any unusual activity in the VDR. If your internal team doesn’t have the expertise to handle this, bring in forensic consultants. To protect sensitive communications during this stage, work with legal counsel under attorney-client privilege and use secure channels like encrypted messaging or secured phone lines if your primary IT systems are still compromised.
Once the investigation reveals the breach’s source and scope, you can shift your focus to addressing the problem.
Take Corrective Actions
Using the findings from the forensic investigation, act quickly to fix the vulnerabilities. Start by changing all administrative rights, passwords, and access codes. Update non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) to include specific remedies for breaches and use tools like user-specific watermarks and stricter data-sharing controls. If specific individuals or vendors were involved in the breach, enforce data destruction clauses in your agreements and request certificates of destruction as proof.
Reconfigure your VDR settings to implement stricter, role-based permissions. For example, restrict non-essential personnel to view-only access and disable the ability to download documents. Additionally, address any legal or regulatory requirements, such as notifying the SEC or local law enforcement, depending on the nature of the incident.
Finally, assess how the breach impacts your deal. If the compromised information affects the valuation or terms, you may need to adjust the purchase price or renegotiate specific provisions to account for the exposed data.
Step 5: Prevent Future Breaches
Once the immediate crisis is under control, the focus should shift to preventing future breaches. This involves upgrading your security systems and ensuring every team member understands their role in safeguarding sensitive data. By combining robust technical measures with proactive team training, you can create a strong defense that protects confidential information over the long term.
Strengthen Security Protocols
Start by implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all platforms that store deal-related data. This extra layer of security makes it much harder for unauthorized users to gain access, even if a password is compromised. Pair MFA with role-based access controls, which limit access to only those who absolutely need it. For instance, junior analysts might only have view-only permissions, while senior team members may receive broader access after completing additional verification steps.
Make sure all data is encrypted both at rest and in transit using industry-standard protocols. To discourage unauthorized sharing, use advanced document watermarking that embeds user-specific identifiers, making it easy to trace leaks back to their source. For particularly sensitive deals, consider setting up clean rooms, which restrict access to a designated “clean team.” This ensures that sensitive data is isolated from decision-makers involved in operational activities.
Keep a close eye on your systems by setting up automated alerts for unusual activity – like excessive file downloads or attempts to access restricted documents. Regularly review audit logs to catch potential insider threats. Recent statistics reveal that nearly 50% of carve-out transactions face active cyber threats during the deal process, highlighting the importance of real-time monitoring.
Train Teams on Confidentiality Best Practices
Even the most advanced technology won’t protect your data without well-trained staff. Provide interactive, role-specific training to ensure every team member understands the importance of confidentiality. Emphasize the need-to-know principle, which limits sensitive information to a small, trusted group. These training efforts should reinforce the security measures you’ve implemented and align with earlier steps in your breach response plan.
Encourage the use of project code names and "blind teasers" (summaries without identifying details) during outreach and internal discussions. Train your team to use encrypted communication tools for all deal-related conversations and remind them to avoid discussing sensitive information in public.
For clean team members, provide specialized training on their specific NDAs. Make it clear that sharing sensitive data with anyone outside the clean team is strictly prohibited. If your team handles SEC filings, teach them how to carefully redact only non-material private terms while securing unredacted versions to avoid accidental disclosures. Lastly, prepare crisis communication scripts so your team knows exactly what to say to employees and customers in the event of a leak.
How Deal Memo Supports Secure CIM/OM Handling
Specialized services like Deal Memo play a pivotal role in reducing risks tied to in-house document creation for Confidential Information Memorandums (CIMs) and Offering Memorandums (OMs). When these documents are prepared internally, the chances of third-party risks increase. Every additional person with access to sensitive data – be it financial information, customer lists, or proprietary processes – raises the likelihood of a breach. Deal Memo addresses this issue by offering white-labeled CIM/OM services that incorporate robust security measures aligned with established best practices for breach prevention. These measures not only enhance overall security but also complement the protocols discussed earlier.
Deal Memo’s Approach to Confidentiality in M&A Transactions
Deal Memo ensures strict confidentiality while delivering CIMs and OMs within 72 hours. Each client is assigned a dedicated account team, which minimizes the number of individuals handling critical information and helps maintain a secure "Circle of Trust."
To further protect sensitive data, Deal Memo employs staged disclosure strategies. For example, early-round documents may redact highly sensitive details – such as customer names or pricing information – until potential buyers have demonstrated their credibility. Additionally, user-specific watermarks are applied to track document distribution and discourage unauthorized sharing. This is especially important given that approximately 95% of confidentiality breaches in M&A transactions stem from within the seller’s organization. By outsourcing CIM/OM preparation to a specialized provider like Deal Memo, companies can significantly reduce their internal exposure and ensure a controlled, secure process.
Customized Solutions for M&A Teams
In addition to its strong confidentiality measures, Deal Memo offers tailored solutions to enhance M&A communications. Investment banking teams can rely on Deal Memo’s white-labeled packages, which ensure consistent branding while offloading the time-consuming task of drafting extensive documents (ranging from 50 to 150 pages). Professionally branded materials not only reflect well on the seller but also signal to buyers that the seller is well-prepared, potentially discouraging aggressive negotiation tactics.
The service includes unlimited calls, meetings, and revisions, as well as seller interviews and Data Room setup. These features are designed to support a disciplined, professional outreach process, significantly reducing the chances of accidental disclosures while maintaining a high standard of communication throughout the transaction.
Conclusion
Confidentiality breaches can throw M&A transactions off course, erode deal value, and strain critical relationships. To tackle these challenges, the guide’s five-step framework – identifying breaches, evaluating their impact, containing the fallout, uncovering the root causes, and implementing safeguards – provides a clear and actionable roadmap to preserve deal integrity.
Confidentiality goes beyond just meeting legal obligations. As PCE Insight aptly puts it:
"Confidentiality isn’t paperwork – it’s a shield that protects your valuation, your people, and your future options".
This quote highlights the importance of treating breach management as a central focus from the very start of any deal. Combining legal measures with operational strategies and personnel protocols is essential to protecting sensitive information.
While the framework lays the groundwork, prevention remains the best defense. Practical steps like creating a "circle of trust", using staged disclosure, and regularly monitoring VDR access logs can significantly lower the risk of breaches. Additionally, having a crisis-response playbook on hand – complete with communication templates for employees, customers, and suppliers – ensures swift action in the event of a leak. One documented case revealed how granting excessive early access led to leaks that forced a rushed deal timeline.
FAQs
What should you do immediately after discovering a confidentiality breach in an M&A transaction?
If you suspect a confidentiality breach during an M&A deal, the first thing to do is verify the breach and understand its extent. Pinpoint what information has been exposed, determine if the breach was accidental or deliberate, and identify whether it originated from internal or external sources. Collect evidence like system logs, email records, or compromised files to aid in your investigation or any legal steps that may follow.
Once you’ve confirmed the breach, initiate your incident response plan. Immediately inform senior legal counsel, lead bankers, and compliance teams to assess the breach’s impact on NDAs or other agreements and to plan a coordinated response. Tighten security by restricting access to sensitive materials – this includes updating permissions in the data room, revoking user access, and resetting passwords or encryption keys. Document every step you take, as these records will be crucial for internal assessments, regulatory reporting, or any legal actions.
How can companies evaluate the financial and reputational impact of a confidentiality breach during an M&A deal?
To gauge the financial impact of a confidentiality breach, companies need to evaluate how the leak influences the deal’s valuation. This typically involves comparing the projected purchase price before the breach with a revised estimate that accounts for potential revenue loss, customer churn, and a diminished deal value. Additionally, factors like regulatory fines, legal expenses, and the scope of the leaked data should be included to calculate the total exposure.
When it comes to the reputational impact, businesses can measure stakeholder trust using surveys, review media coverage, and analyze sentiment on social media platforms. Publicly traded companies might notice immediate outcomes such as stock price fluctuations or a drop in share value, reflecting the market’s perception of reputational harm. Internally, organizations should assess risks like increased employee turnover or the departure of key personnel, as breaches often erode morale and trust within the workforce.
By integrating financial evaluations with reputation analysis, companies can create a comprehensive impact assessment. This approach not only informs their response strategies but also helps reinforce confidentiality measures moving forward.
What steps can be taken to prevent confidentiality breaches in M&A transactions?
Preventing confidentiality breaches during M&A transactions calls for a mix of legal, technical, and operational strategies. A good starting point is crafting customized non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) for all parties involved. These agreements should clearly outline what information is protected, how it can be used, and the penalties for any breaches. On the technical side, restrict access to sensitive information by implementing role-based permissions, multi-factor authentication, and encrypted virtual data rooms for sharing documents. It’s also crucial to monitor access logs regularly for any unusual activity and ensure that all communications happen over secure channels, such as password-protected links or encrypted emails.
From an operational perspective, staged disclosures or "clean-team" structures can help control who has access to specific details. In the early stages, you might use code names or blind teasers to keep critical information under wraps. Even after the deal is finalized, maintaining strict access controls and comprehensive audit trails can help prevent leaks. Tools like Deal Memo can also simplify the process of creating secure and polished Confidential Information Memorandums (CIMs), reducing the risk of accidental exposure. By combining these approaches, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of confidentiality breaches during M&A transactions.