Virtual data rooms (VDRs) are secure online platforms designed for managing sensitive documents, particularly in high-stakes deals like mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Unlike general file-sharing tools, VDRs offer advanced features like encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access controls to ensure confidentiality.
Key takeaways:
- Encryption: AES-256 secures data both at rest and in transit.
- MFA: Adds extra protection by requiring multiple verification steps.
- Access Controls: Permissions are tailored to user roles to limit unnecessary exposure.
- Document Protections: Features like watermarking, DRM, and redaction prevent unauthorized sharing.
- Monitoring Tools: Audit trails log every action, helping detect and prevent breaches.
Confidentiality is critical, as data breaches cost U.S. businesses an average of $9.36 million in 2024. Human error is a leading cause, making user training and strict internal policies essential. Legal safeguards like NDAs and phased access strategies further reduce risks. By combining advanced technology with proactive governance, businesses can protect sensitive data effectively.
Security measures in virtual data rooms
Technical Security Measures for Data Protection
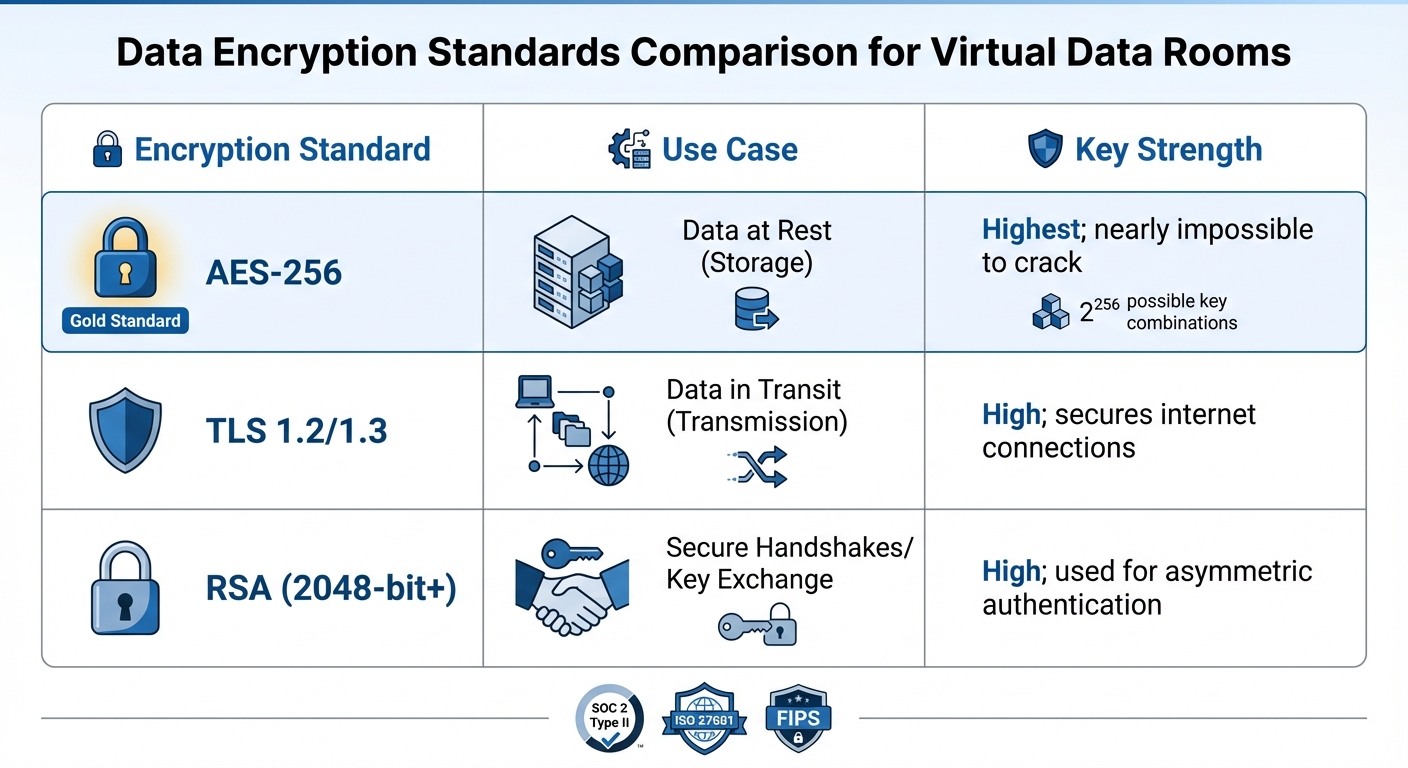
Data Encryption Standards Comparison for Virtual Data Rooms
Data Encryption Standards
When it comes to safeguarding data in virtual data rooms (VDRs), AES-256 encryption stands out as the gold standard. This method uses a 256-bit key to convert readable data into unreadable ciphertext, offering an astronomical 2^256 possible key combinations. In practical terms, cracking this encryption through brute force is virtually impossible.
For optimal security, your VDR should encrypt data in two key states: at rest (stored on servers) and in transit (moving between users). Data in transit is protected by Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols, which not only encrypt the data but also authenticate both senders and recipients. High-security VDRs often meet FIPS standards to ensure maximum protection.
| Encryption Standard | Use Case | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|
| AES-256 | Data at Rest (Storage) | Highest; nearly impossible to crack |
| TLS 1.2/1.3 | Data in Transit (Transmission) | High; secures internet connections |
| RSA (2048-bit+) | Secure Handshakes/Key Exchange | High; used for asymmetric authentication |
To ensure comprehensive security, look for VDRs that implement dual encryption for both data states, supported by rigorous key management practices and certifications like SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001. Once encryption is in place, strong authentication measures further fortify data protection.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Encryption alone isn’t enough; multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another critical layer of defense. MFA requires users to verify their identity using at least two methods – such as something they know (a password), something they have (an authenticator app or physical token), or something they are (biometric data). This approach significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
A cautionary tale: between 2013 and 2015, Evaldas Rimasauskas exploited weak MFA protocols to defraud Facebook and Google of over $100 million. This underscores the importance of robust MFA in high-stakes environments.
For better security, opt for authenticator apps rather than SMS codes, which can be intercepted. Additionally, combine MFA with automatic session timeouts to prevent misuse if someone leaves their device unattended. Many modern VDRs integrate MFA with role-based permissions and session controls, creating a "Zero Trust" model that requires continuous verification.
Access Controls and User Permissions
Encryption and authentication are vital, but access controls ensure that only the right people can view or interact with sensitive documents. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) assigns permissions based on a user’s job function, adhering to the principle of least privilege – granting access to only what’s necessary for their role.
Administrators can fine-tune permissions for each document, setting specific rights like view-only, edit, download (original or encrypted), print, and copy/paste. For added security, IP-based restrictions block access from unauthorized locations, even if login credentials are compromised. Temporary collaborators can be managed with time-limited access, which automatically revokes permissions after a set period.
To ensure permissions are configured correctly, administrators can use the "View As" mode to see the data room from a specific user’s perspective. This feature is particularly useful when managing complex projects involving multiple parties. Regular permission audits are also crucial, especially after organizational changes.
For advanced security, features like fence view block parts of documents to prevent screen captures, while remote shredding can revoke access to files even after they’ve been downloaded to a user’s device.
Document Protection Features
Dynamic Watermarking
Dynamic watermarking embeds user-specific details – like email addresses, IP addresses, and timestamps – directly onto documents in real time. This makes each watermark unique to the user accessing the document, unlike static watermarks that remain the same for everyone. By linking identifiable information to specific users, this approach discourages unauthorized sharing.
The visible association of a user to a document creates a strong psychological and practical deterrent. Experts note that including personal identifiers in watermarks introduces both social and forensic barriers, reducing the likelihood of misuse.
When setting up watermarks, it’s important to strike the right balance between visibility and usability. For example, in M&A transactions involving external bidders, you might want to increase the watermark’s density and opacity to make it more noticeable. On the other hand, for internal reviewers, subtler watermarks can minimize disruption to their workflow. Advanced systems can even detect attempts to tamper with or remove watermarks, automatically revoking access for those users.
After applying watermarks, Digital Rights Management (DRM) takes document protection a step further by securing the document itself.
Digital Rights Management (DRM)
DRM embeds security features directly into documents, ensuring protection even after they’ve been downloaded. This includes blocking actions like copying, editing, printing, and using screen-capture tools. Essentially, DRM ensures that the document’s security remains intact wherever it goes.
For instance, DRM can disable features like "Print to PDF" to prevent workarounds. Additionally, modern DRM solutions allow you to restrict document access to specific devices or locations, set expiration dates, and revoke access immediately if needed.
"DRM controls are needed to deliver a properly secure data room… you can prevent people from making unauthorized copies of documents or from saving them and then forwarding on." – Locklizard
For even greater security, DRM can be combined with a "fence view" feature. This feature places a digital sliding bar over most of the screen, following the user’s cursor to block unauthorized screen captures or prying eyes during sensitive negotiations.
While DRM safeguards the document as a whole, redaction tools focus on protecting specific pieces of sensitive information.
Redaction Tools
Redaction tools allow you to permanently remove sensitive information – such as social security numbers, trade secrets, or privileged legal content – before sharing documents with specific groups. This feature is especially useful for documents that contain both confidential and non-confidential sections, enabling selective sharing without compromising security.
To avoid common mistakes, ensure that redaction tools completely remove both the visible text and any underlying text layers. Failing to do so, often referred to as the "text layer trap", can leave sensitive information vulnerable to recovery.
Before finalizing access, use the "View As" feature to confirm that redacted documents appear correctly to different recipient groups. Additionally, document the reason for each redaction – such as "Attorney-Client Privilege" or "PII" – to maintain an audit trail. This can be critical for supporting clawback requests if sensitive information is mistakenly disclosed.
Activity Monitoring and Audit Trails
Activity Logging and User Tracking
In a virtual data room, every action is meticulously recorded in an audit trail. This includes details like who performed the action, what they did, when it happened, and the result. Activities such as document views, downloads, prints, edits, and administrative changes (like updating user permissions or inviting new users) are all logged. Engagement metrics, such as time spent on individual documents, are also tracked to identify unusual patterns, like rapid, high-volume downloads.
This detailed tracking not only helps assess genuine interest during transactions but also acts as a safeguard against suspicious behavior.
"Data rooms offer transparency and accountability by tracking every action with detailed audit trails, recording who accesses documents and what changes they make." – Editorial Team, Data-rooms.org
Organizations equipped with effective monitoring tools can detect data breaches 33% faster than those without. Considering that the average cost of a data breach in the U.S. climbed to $9.36 million in 2024, having comprehensive tracking measures in place is crucial.
To enhance security, configure your system to send real-time alerts for high-risk activities, such as unauthorized access attempts. Automating regular activity reports can also help maintain oversight without adding manual tasks. Be sure to retain audit logs for at least 90 days, or longer if required by regulations like HIPAA or GDPR.
Pairing audit trails with strong version control ensures document accuracy and reliability.
Version Control
Version control ensures that users always have access to the most current documents while keeping a complete archive of all previous revisions. Every time a document is updated, the system automatically saves the older version, reducing the risk of errors caused by outdated files.
Each revision is timestamped and linked to the user who made the change, creating a clear record of document history. This is especially important for M&A transactions and legal discovery processes. To keep your workspace organized, consider archiving older versions in a clearly labeled folder while maintaining the full audit history.
Standardized naming conventions and automated notifications help ensure all users are aware of the latest approved version. For added accuracy, use "View As" to verify how the document appears in its final form.
sbb-itb-798d089
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Compliance Frameworks
Virtual Data Rooms (VDRs) must align with key regulatory standards to ensure security and trust. One of the most recognized frameworks is SOC 2, established by the AICPA. This standard evaluates five critical Trust Services Criteria: Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. A SOC 2 Type II report is particularly rigorous, as it assesses how controls operate over a period of 3 to 12 months, demonstrating not just their design but also their effectiveness over time.
In the healthcare sector, HIPAA and the HITECH Act are pivotal. These regulations require robust safeguards to protect electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). The HITECH Act enhanced HIPAA by extending its Security Rule to business associates, including VDR providers, and introduced stricter penalties for violations. Healthcare organizations must ensure their VDR providers sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) and retain relevant documentation for at least six years.
Another widely respected standard is ISO/IEC 27001, which offers a framework for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). Certification under this standard highlights a commitment to regular security audits and proactive risk management. For federal agencies and contractors, FISMA compliance is mandatory, requiring robust security controls and continuous monitoring. Businesses in California face additional obligations under the CCPA, which grants residents strong data privacy rights.
Here’s a quick breakdown of key compliance frameworks and their focus areas:
| Framework | Primary Focus | U.S. Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| SOC 2 | Security, Confidentiality, Privacy | Service providers (e.g., SaaS, Cloud, VDRs) |
| HIPAA/HITECH | Protection of ePHI | Healthcare providers, plans, business associates |
| ISO 27001 | Information Security Management | Global/Voluntary (often required by enterprises) |
| FISMA | Federal Information Systems | Federal agencies and government contractors |
| PCI-DSS | Credit Card Data Security | Entities processing card payments |
| CCPA | Consumer Privacy Rights | Organizations handling California residents’ data |
The stakes for non-compliance are high. For example, GDPR violations can result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is greater. The financial and reputational risks make compliance a non-negotiable priority.
To meet these regulatory demands, organizations must implement strong data governance practices that integrate seamlessly with their compliance strategies.
Data Governance Policies
A solid data governance strategy begins with a thorough data audit, classification, and lifecycle mapping. This process helps identify appropriate retention periods and disposal protocols for different types of documents.
"Virtual data room compliance requires a systematic 6-step approach encompassing regulatory understanding, data auditing, security implementation, policy development, ongoing reviews, and breach preparedness to ensure adherence to global data privacy laws." – Danielle Barbour, Regulatory Compliance Expert, Kiteworks
Implementing granular access controls is crucial. Role-based permissions ensure users only access the information they need for their specific tasks, reinforcing security measures. For example, the FTC Safeguards Rule mandates that financial institutions designate a qualified individual to oversee their information security program. It also requires multi-factor authentication for accessing customer information. Regular security assessments, such as annual penetration tests and biannual vulnerability scans, are essential to identify and address potential weaknesses.
Automation can further enhance governance. Automating document retention and disposal processes supports data minimization principles, while immutable, timestamped audit trails provide verifiable evidence during regulatory audits. Before undergoing formal audits, organizations should perform internal gap analyses to identify and address any shortcomings in their compliance measures.
User Training and Internal Policies
Staff Training on Data Security
Technical defenses like encryption and access controls are crucial, but they can only go so far if employees aren’t trained to recognize security threats. For instance, phishing emails or poor password practices can undermine even the most advanced systems.
Training programs should focus on phishing and social engineering tactics to help employees spot fraudulent emails and phone scams. This is critical, as 81% of cyberattacks stem from phishing, weak passwords, and malware. Employees also need to understand the risks of reusing passwords – 52% of people reuse them across accounts, which can lead to a chain reaction of breaches if one account is compromised.
Hands-on training is equally important. Employees should learn practical skills like applying dynamic watermarking, redacting personally identifiable information (PII), and setting view-only restrictions on sensitive files. Administrators, in particular, need to understand role-based access controls, the risks of permission inheritance in subfolders, and how to use "View As" tools to verify what external collaborators can access.
"As much as 74% of all data breaches involve a human element." – DataRooms.org
To reinforce these practices, organizations should implement mandatory VDR security training during onboarding. This training should include role-specific materials like quick-start guides and video tutorials. Regular permission audits are also necessary to prevent "access creep", where users retain permissions they no longer need.
Legal protections, such as Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), add another layer of security, as detailed below.
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
NDAs act as a legal safeguard, ensuring that users commit to confidentiality before gaining access to sensitive information. Given the financial risks associated with data breaches, a well-crafted NDA provides a clear path for legal recourse if confidentiality is breached.
To streamline this process, integrate NDAs into the VDR workflow by requiring users to sign digitally upon their first login. Use eSignature platforms that comply with the U.S. E-SIGN Act to ensure enforceability. These platforms should also maintain detailed audit trails, including timestamps, IP addresses, and verification logs.
A strong NDA clearly defines what qualifies as confidential – such as trade secrets, financial data, or intellectual property – while excluding publicly available information. It should also include survival clauses to extend confidentiality obligations beyond the end of a project or business relationship. While standard NDAs typically last between one and five years, protections for trade secrets can extend indefinitely.
"Now is the perfect time for in-house counsel to focus on how best to use electronic signatures at your company… just make sure you are truly up-to-speed on the laws in your jurisdiction and that you have the right systems and procedures in place." – Sterling Miller, CEO and Senior Counsel, Hilgers Graben PLLC
Phased Access Strategies
To further minimize risk, phased access strategies limit exposure by gradually revealing sensitive information as a transaction progresses. Instead of granting full access immediately, sensitive data is disclosed only to vetted parties who meet specific criteria. For example, early-stage bidders might receive high-level summaries, while finalists gain access to detailed documents like intellectual property or employee contracts.
Access levels should align with key deal milestones, such as signing an NDA or submitting a Letter of Intent (LOI). For particularly sensitive data, consider using clean rooms, which restrict access to a select group of third-party experts. Permissions should also be time-bound, automatically expiring after a set period or specific date to ensure access doesn’t extend unnecessarily.
Organizations with strong monitoring and auditing tools can detect breaches 33% faster than those without such capabilities. Before advancing to a new phase, use "View As" tools to confirm that users only see what they’re authorized to access at that stage. Beyond folder-level controls, apply file-specific restrictions to disable printing, downloading, or copying of sensitive materials.
Conclusion
Summary of Best Practices
Keeping confidential data secure in a virtual data room requires a combination of advanced technology, clear procedures, and consistent practices. Start with strong encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and tight access controls. Add document-specific protections like dynamic watermarking, Fence View, and Remote Shred – these not only deter unauthorized sharing but also provide a clear trail in case of leaks. Comprehensive audit trails, detailing who accessed what, when, and for how long, are essential for identifying suspicious activity quickly.
"The objective of data room security is to balance the need for data protection with authorized users’ need to access, share, and collaborate with sensitive information." – Egnyte
Technology alone isn’t enough – human factors also play a big role. Regular training on recognizing phishing attempts, creating secure passwords, and handling sensitive documents properly can significantly reduce the risk of errors. Implement phased access to limit exposure during transactions, and use legal safeguards to strengthen protection. By combining these technical tools with ongoing employee training and legal measures, you can build a solid strategy for maintaining data room confidentiality.
Implementation Steps
Putting these best practices into action starts with a clear plan. First, conduct an inventory of all documents and categorize them by sensitivity – High, Medium, or Low – so you can apply the appropriate security measures. When choosing a virtual data room provider, confirm they hold certifications like SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA. With the average cost of a data breach in the U.S. climbing to $9.36 million in 2024, selecting a provider with proven credentials is critical.
When setting up your data room, create a simple 2–3 level folder structure and use consistent naming conventions (e.g., "Balance_Sheet_2024_v1.pdf"). Before launching, test permissions using a "View As" feature to ensure proper access levels. Configure automatic session timeouts and set expiration dates for external access to minimize prolonged exposure.
After the data room is live, establish a routine for maintenance. Schedule monthly audits to remove inactive accounts and update permissions as roles change. Regularly review activity logs for signs of unusual behavior, such as large downloads or access attempts during off-hours. These proactive steps help ensure your data stays secure while remaining accessible to authorized users.
FAQs
What makes AES-256 encryption a reliable choice for securing virtual data rooms?
AES-256 encryption protects data by employing a 256-bit symmetric key to convert sensitive information into unreadable ciphertext. This means the data remains secure and can only be unlocked using the correct key, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to access.
Thanks to its strong encryption standard and lengthy key, AES-256 is widely regarded as one of the most reliable ways to secure files in virtual data rooms. It ensures that documents stay confidential, whether they’re being stored or transmitted.
Why is multi-factor authentication important for securing virtual data rooms?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) plays a key role in protecting virtual data rooms by adding an extra layer of security. It requires users to confirm their identity through multiple factors – like a password, a mobile device, or biometric data. This approach makes it much harder for unauthorized users to gain access, even if a password gets compromised.
MFA is also effective against phishing and social engineering attacks. Simply put, stolen login credentials alone won’t be enough to breach the system. For high-stakes transactions, it ensures that only verified users can access sensitive documents, blocking any unauthorized attempts. This added security offers peace of mind for dealmakers handling confidential information.
Why are regular audits and monitoring essential for maintaining data room security?
Keeping a close eye on your data room through regular audits and activity monitoring is essential for maintaining security. These practices provide ongoing visibility into how documents are accessed and used, making it easier to spot unauthorized access, unusual behavior, or any lapses in following security protocols.
A detailed, unalterable audit trail serves as a powerful tool to address potential weak spots quickly, safeguard sensitive data, and ensure your data room remains secure and runs smoothly.